- What is a company worth?
- Why company value matters?
- The value of a future dollar
- Intrinsic value
- Book value
- Market capitalization
What is a company worth?
Suppose there is a company that consistently generates \$1 per year. What is that company worth?

Why company value matters?
What the stock market says a company is worth is often different than what a company is actually worth. On one particular day, the stock market might overvalue a company; on another, it might undervalue the company.
Many trading strategies focus on identifying where the current stock price diverges from the true value of the company. For example, if we see a stock price that surpasses this value, we know to sell the stock. Conversely, a stock price that falls below this value signals that we should buy the stock.
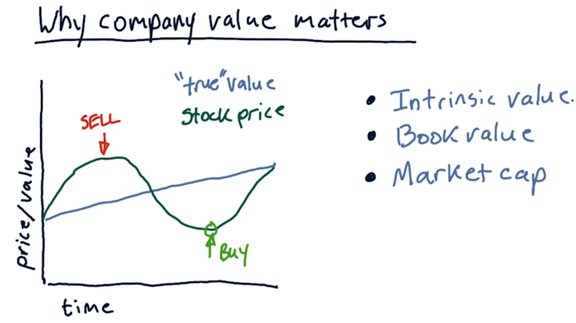
Three ways to evaluate the stoce value:
- Intrinsic value
- Book value
- Market cap
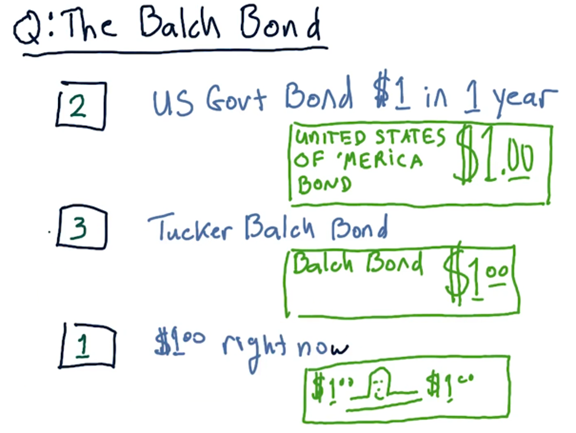
The Balch Bond Quiz
Assume that we are in a position to receive one of three different assets.
The first asset is a \$1 bill: cold, hard cash. The second asset is a Tucker Balch bond; essentially, a promise certified by the professor that he will pay us \$1 in one year. The third asset is a US Government bond, which also pays out \$1 in one year, but is backed by the United States government.
Which of these assets would you rather receive? Rank the choices from 1 (best) to 3 (worst).
The value of a future dollar
We need to account for two factors when thinking about the value of a promised dollar: who is making the promise and how long we have to wait for them to deliver the dollar.
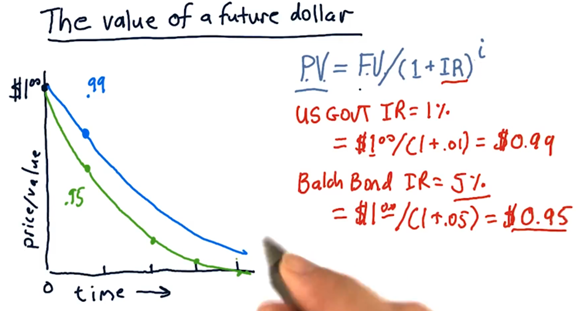
PV: present value; FV: future value; IR: interest rate; i: waiting period, measured in i years
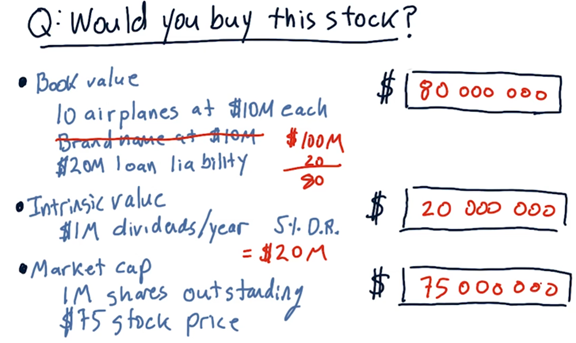
Intrinsic value
Intrinsic value uses dividends to measure the value of a company.
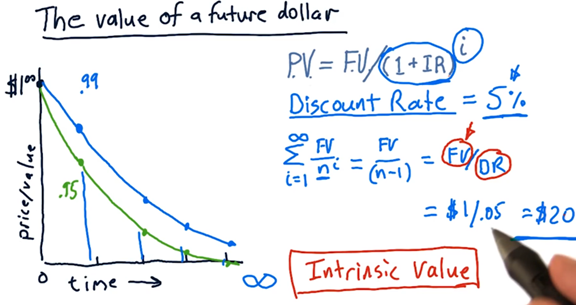
We can compute the present intrinsic value, IV, of the whole company by taking the sum of the present values of all dividends to be distributed.
Instead of interest rate, we consider the discount rate, which is a measure of how risky we think an investment in a company might be.
For example: If the dividend = \$2/ year, and the discount rate = 4% ===> Intrinsic value = 2/0.04 = \$50.
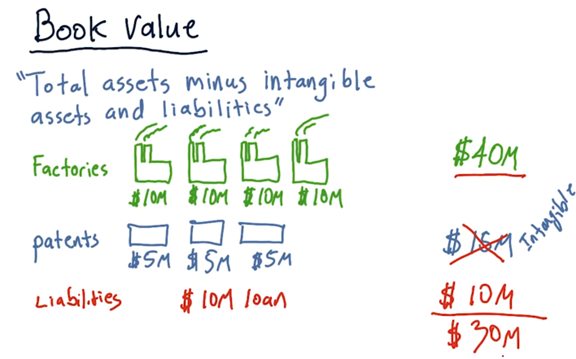
Book value
A classic definition of book value is total assets minus intangible assets and liabilities.
Market capitalization
Alternatively, we can let the market determine the value of a company. Market capitalization is the product of the number of outstanding shares and the share price.

For instance, a company with 1,000,000 shares and a share price of \$100 has a market capitalization of \$100,000,000.
Compute company value quiz